
Choosing the right drill bit sharpening angle is crucial for efficient drilling and the longevity of your tools. The angle you select can make a significant difference in performance and durability, ensuring that your projects are completed smoothly and effectively.
The sharpening angle of a drill bit affects its cutting efficiency and lifespan. A proper angle enhances drilling speed, reduces material resistance, and extends the bit’s usability. Selecting the right angle is essential for different materials and drilling applications. Understanding drill bit angles helps you make informed decisions in your projects, leading to better results and fewer frustrations.
Do You Know the Angle of HSS Drill Bits?
What is the standard angle for HSS drill bits?
High-Speed Steel (HSS) drill bits typically have a standard point angle of 118 degrees. This angle is versatile and works well with a variety of materials, making it a popular choice for many drilling tasks. However, it’s important to note that while the 118-degree angle is widely used, it may not be suitable for all materials and applications. Understanding the limitations and optimal uses of this angle can help you choose the right drill bit for your specific needs.

Delving into the standard angles of HSS drill bits can enhance your drilling accuracy and tool performance, ensuring that you get the best results from your tools.
Why 118 Degrees is the Standard Angle for HSS Drill Bits
The 118-degree angle1 strikes a balance between cutting performance and durability. It’s ideal for softer materials like mild steels and cast irons, providing efficient drilling without excessive wear. This balance makes the 118-degree angle a reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
- Cutting Efficiency: The 118-degree angle is optimized for a wide range of materials, ensuring smooth and fast drilling. This efficiency translates to less time spent on each task and more consistent results.
- Durability: This angle reduces wear and tear, extending the life of your drill bits. With less frequent need for sharpening or replacement, you can maintain productivity without interruptions.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, minimizing the need for multiple drill bits. Whether you’re working on metal, wood, or other softer materials, the 118-degree angle serves as a dependable option.
HSS Drill Bit Angle Selection
| Angle (Degrees) | Suitable Materials | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| 118° | Mild steels, cast irons | Efficient cutting, durable, versatile |
| 135° | Harder steels | Enhanced penetration, reduced work hardening |
While the 135-degree angle offers benefits for harder steels, it’s important to recognize that HSS (twist) drill bits are not suitable for cutting ceramics or drilling into rebar. These materials require specialized drill bits designed to handle their hardness and composition. Using an HSS drill bit on ceramics or rebar can lead to poor performance, increased wear, and potential tool damage.
Choosing the right angle can significantly improve your drilling results and tool longevity. However, always consider the material you’re working with and whether an HSS drill bit is the appropriate choice.
Personal Insights
I’ve often found myself in situations where selecting the right drill bit angle made all the difference in my projects. For instance, when working on a mild steel frame for a workshop, the 118-degree angle provided the perfect balance between speed and precision. It allowed me to drill holes quickly without compromising the quality of the work. On the other hand, when faced with harder steels, switching to a 135-degree angle significantly improved my drilling efficiency.
118° or 135° for Larger HSS Drills?
When dealing with larger HSS drills, which angle should you choose: 118° or 135°?
For larger HSS drills, a 118-degree angle is suitable for most metals and wood, while a 135-degree split point is ideal for harder steels and deep holes over four times the drill diameter. Understanding the specific applications of each angle helps in selecting the right drill bit for your larger projects, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
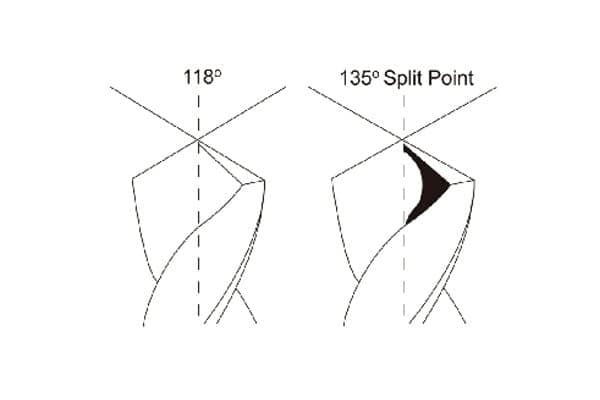
Understanding the specific applications of each angle helps in selecting the right drill bit for your larger projects, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Comparing 118° and 135° Angles for Large Drills
The 118-degree angle is great for general-purpose drilling, providing stability and efficiency in softer materials like mild steels2 and cast irons. Its design allows for smooth cutting and minimal wear, making it a reliable choice for everyday tasks.
On the other hand, the 135-degree split point excels in cutting harder steels, offering enhanced penetration and reduced work hardening. This angle is particularly beneficial when drilling deep holes, as it produces thicker chips that minimize the work hardening of the cavity short.
Selection Recommendations
Selecting the appropriate angle based on your drilling needs ensures optimal performance and tool longevity. For most metal and wood drilling tasks, the 118-degree angle provides the necessary efficiency and durability. However, for harder steels and situations requiring deep drilling, the 135-degree angle offers significant advantages.
Practical Example
In my experience, switching to a 135-degree split point when drilling into hardened steel made a significant difference. The thicker chips reduced clogging and heat buildup, allowing for smoother and more precise drilling. This change not only improved the quality of my work but also extended the life of my drill bits.
Why Standard Tip Angle is 118 Degrees?
Why has the 118-degree angle become the standard for drill bit tips?
The 118-degree angle offers an optimal balance between cutting efficiency and drill bit longevity, making it the preferred choice for a wide range of drilling applications. This standardization simplifies the selection process for users, ensuring that a single angle can effectively handle most common drilling tasks.

Exploring the reasons behind the 118-degree standard helps in appreciating its widespread use and effectiveness, as well as understanding its limitations.
Advantages of the 118-Degree Angle
The 118-degree angle excels in providing efficient cutting performance across various materials while maintaining durability. It’s particularly effective for softer materials3, ensuring clean and precise holes without excessive wear.
- Efficient Cutting: Optimized for a range of materials, ensuring smooth and fast drilling. This efficiency translates to less time spent on each task and more consistent results.
- Durable Performance: Reduces wear and tear, extending drill bit life. With less frequent need for sharpening or replacement, you can maintain productivity without interruptions.
- Wide Applicability: Suitable for multiple materials, minimizing the need for different bits. Whether you’re working on metal, wood, or other softer materials, the 118-degree angle serves as a dependable option.
However, it’s important to remember that while the 118-degree angle is versatile, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. For materials like ceramics and rebar, specialized drill bits are necessary to achieve effective drilling without damaging the tools or the materials.
Real-World Applications
In construction and manufacturing, the 118-degree angle is a go-to choice for drilling into metal and wood. Its reliability in providing consistent results makes it indispensable for both professional and DIY projects.
| Application Sector | Specific Use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Machining parts | Efficient cutting, long-lasting |
| DIY Projects | Building furniture | Versatile use, easy handling |
Using the 118-degree angle ensures that you have a dependable tool for a variety of drilling tasks, enhancing both productivity and quality. For instance, when building furniture, the 118-degree angle provides clean and accurate holes, allowing for precise assembly and a professional finish.
Which Drill Point Angle Should I Use?
How do you decide which drill point angle is best for your needs?
Choosing the right drill point angle depends on the material you’re working with and the specific requirements of your drilling task. Understanding the benefits of each angle helps in making the best choice for your projects. This decision is crucial for achieving optimal results, whether you’re working on a simple home project or a complex industrial task.

Knowing which angle to use ensures that you achieve the best results, whether you’re drilling into metal, or other materials.
Drill Point Angle Selection Guide
When selecting a drill point angle, consider the following factors:
- Material Type: Different materials require different angles for optimal drilling. Softer materials like mild steel and wood are well-suited for a 118-degree angle, while harder steels benefit from a 135-degree angle. However, for ceramics and rebar, specialized drill bits are necessary.
- Drilling Depth: Deeper holes may benefit from a steeper angle like 135 degrees, which facilitates better chip removal and reduces work hardening.
- Precision Needs: High-precision tasks might require specific angles to ensure accuracy and clean cuts. The 118-degree angle is generally sufficient, but more specialized tasks may demand different specifications.
Common Drill Point Angles and Their Uses
| Angle (Degrees) | Suitable Materials | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 118° | Metals, Wood | Efficient cutting, versatile use |
| 135° | Hard materials, Steels | Enhanced penetration, reduced work hardening |
It’s important to note that HSS (twist) drill bits are not suitable for ceramics or drilling into rebar. For ceramics4, diamond-tipped drill bits are recommended, while rebar drilling typically requires specialized masonry bits or rotary hammer drills.
Practical Tips
- Identify the Material: Know what you’re drilling into to choose the right angle. For example, use a 118-degree angle for mild steel and wood, and a 135-degree angle for harder steels.
- Assess the Task: Determine the depth and precision required for your drilling. Deeper holes may benefit from a steeper angle, while high-precision tasks may require more careful angle selection.
- Choose Accordingly: Select the angle that best matches your material and task needs. If you’re working with ceramics or rebar, invest in the appropriate specialized drill bits instead of relying on HSS bits.
By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the most effective drill bit angle for your specific project, leading to better results and longer-lasting tools.
Anecdote
Once, I was faced with drilling a deep hole in hardened steel for a custom project. My usual 118-degree bit struggled, producing thin chips and overheating. Switching to a 135-degree split point made the process much smoother. The thicker chips reduced clogging and heat buildup, allowing me to complete the task efficiently and with cleaner results. This experience highlighted the importance of selecting the right angle for the material and task at hand.
Conclusion
Choosing the right drill bit angle can significantly improve your drilling performance and tool longevity. Understanding the benefits of 118° and 135° angles helps you make informed decisions for various materials and applications. Remember, while HSS (twist) drill bits are versatile, they are not suitable for all materials, such as ceramics and rebar. Selecting the appropriate drill bit for your specific needs ensures efficiency, quality, and durability in your projects.
-
Understand why this specific angle is preferred in cutting tools, providing insights into its advantages in performance and durability. ↩
-
Explain why it’s ideal for specific drilling tasks and how it interacts with cutting tools. ↩
-
Softer materials benefit from a 118-degree angle, aiding in selecting the right tools for specific projects. ↩
-
Ensuring they use the right tools to prevent damage and achieve clean cuts. ↩